Experience Center
About Threat Categories
Threat categories group common threats (e.g., viruses, botnets, exploits) together. Zscaler's Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) uses signature-based detection to identify and control these threats. Zscaler provides a number of predefined threat categories, each associated with a collection of custom IPS signature rules, which are like fingerprints of known network attack patterns. In addition to the predefined threat categories, you can define custom threat categories with custom signature rules that are specific to your organization’s requirements. Using these threat categories, you can define IPS Control rules to monitor and protect your network traffic against malicious activities.
- See the list of predefined threat categories and their description.Close
Threat Category Description Advanced Security Threats not included in the other threat categories. Adware/Spyware Sites Adware or spyware displays malicious advertisements that can collect users' information without their knowledge. Anonymizer Anonymizer (or anonymous proxy) is a proxy server that makes your internet activities untraceable. It acts as an intermediary between a client and the internet and protects the identity of the user that is accessing the internet. While anonymizer has several positive applications, it can be effectively used for malicious purposes, such as slander, threat, harassment, illegal acts, etc. Application Detection (TOR, Ultrasurf, VPN apps etc) Traffic patterns that belong to the fingerprints of a specific application. Reconnaissance Attempts Reconnaissance attacks comprise a variety of techniques used to obtain information about a target organization's systems and networks that aids in planning and launching cyberattacks against the organization. Examples of reconnaissance attacks include packet sniffing, port scanning, OS fingerprinting, social engineering, etc. Botnet Callback Botnets are systems in which attackers have secretly installed their software. This software is designed to communicate periodically with a "command and control" center, and a master application instructs the infected computers to send spam, phishing email, or perform other malicious tasks. Browser Exploit Browser exploits are web browser vulnerabilities that can be exploited, including exploits for Internet Explorer and Adobe Flash. Brute Force Attack Brute force attacks use the trial and error method to crack passwords, passphrases, login credentials, and encryption keys and gain unauthorized access to individual user accounts or an organization's systems and networks. The attacker systematically tests different combinations of characters against the target until obtaining a successful login, often using tools such as bots and scripts. Cross-site Scripting Cross-site scripting (XSS) refers to vulnerabilities in web server applications that allow malicious users to inject their own code into the website. Crypto Mining Most organizations prefer to block crypto mining traffic prevent cryptojacking, malicious scripts or programs that secretly use the device to mine cryptocurrency. For example, JavaScript in a compromised website, banner, or ad can use the browser to mine cryptocurrency and harm the user's device. However, in some cases, blocking this traffic might cause certain sites that use crypto mining as a source of income to stop working. It might also interfere with legitimate attempts to use cryptocurrency for payments. Denial of Service Attack A Denial of Service attack is an attack where a computer or internet connection attempts to overload a system, network, or application. Domain Generation Algorithm (DGA) Domains Domains that are suspected to be generated using domain generation algorithms. These algorithms are used in various malware families to periodically generate a large number of domain names that can be used by malware-infected devices to connect with command and control servers in order to circumvent the identification and shutting down of malicious domains. Exploit An exploit is an attack where known non-web (non-HTTP) vulnerabilities are exploited. Malicious Content Malicious content includes websites that attempt to download dangerous content to your browser when you visit them. Increasingly, this content is downloaded silently without the user's knowledge or awareness. Malicious sites include exploit kits, compromised websites, and malicious advertising. Malware Malware (or malicious software) is any program or file that is designed to infiltrate, damage, and exploit a computer, server, client, or network.
Malware detection refers to monitoring your network traffic and identifying the presence of malware using signatures.Peer-to-Peer Peer to peer refers to internet resources that allow users to easily share files with each other. The danger is that users may illegally share copyrighted or protected content. Phishing Phishing sites are websites that mimic legitimate banking and financial sites (for example, Citibank.com, PayPal.com, and so on). Their purpose is to deceive you into thinking you can safely submit bank account, password, and other personal information which criminals can use to steal your money. Policy Violation Traffic that could potentially violate the corporate policy. Ransomware Ransomware is a type of malicious software that holds a user’s sensitive information or an organization’s critical data for ransom. Ransomware often uses encryption to deny users access to their critical data and/or threaten to publish the data. Risky Behaviors Includes IPS signatures that are considered risky but might have some legitimate usage (e.g., signatures for websockets-to-SSH detections as in the case of Chisel usage). Signatures in this threat category can cover a wide range of detections and might include legitimate traffic, as well. Therefore, organizations might want to exclude this threat category from being blocked for users by creating a higher order IPS rule with the Risky Behaviors threat category as a condition and the action set to Allow or Bypass IPS. Suspected Spyware or Adware Sites that display characteristics of spyware/adware sites Suspicious Destinations Suspicious destinations include the following URL categories:
- Nudity
- Pornography
- Anonymizer
- FileHost
- Shareware
- Download
- Web Host
- Miscellaneous or Unknown
- Other Miscellaneous
Unauthorized Communication Unauthorized communications refer to IRC tunneling applications and "anonymizer" sites that are used to bypass firewalls and proxies. Webspam Web spam includes web pages that pretend to contain useful information, to get higher ranking in search engine results or drive traffic to phishing, adware, or spyware distribution sites.
Threat Categories provide the following benefits and enable you to:
- Define the IPS Control policy using a collection of signature rules that identify patterns associated with attacks, exploits, and malicious behaviors and protect your network from malicious activities.
- Enhance IPS capabilities by creating new threat categories using custom IPS signature rules specific to your organization requirements.
- Investigate and analyze the threats detected in your network by leveraging Zscaler Firewall logs. Use Zscaler-generated logs as a source of signal generation in SIEM, XDR, and other threat intelligence systems.
You can add a maximum of 64 custom threat categories.
About the Threat Categories Page
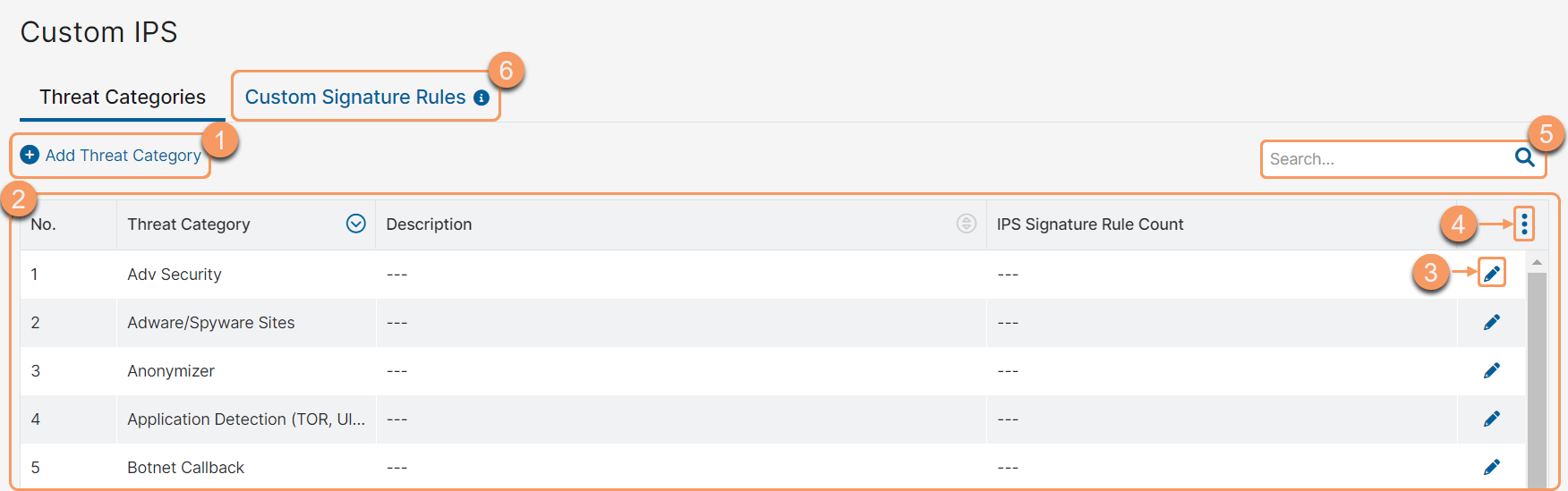
On the Threat Categories page (Policies > Cybersecurity > Inline Security > Custom IPS Signatures > Threat Categories), you can do the following:
- Add a custom threat category.
- View a list of all threat categories, including predefined and custom threat categories. By default, the table displays the following:
- Threat Category: The name of the threat category. You can sort this column.
- Description: The description of the threat category.
- IPS Signature Rule Count: The number of custom signature rules that are included in the threat category.
- Edit a threat category. This action also allows you to delete a threat category.
- Modify the table and its columns.
- Search for a threat category.
- Go to the Custom Signature Rules page to add and manage custom signature rules.