Experience Center
About DNS Gateways
DNS Gateway extends the capabilities of DNS Control by including support for DNS high availability and translation of protocols to perform DNS lookup by external DNS services. You can ensure the high availability of your DNS service by configuring primary and secondary DNS services provided by third-party DNS services. You can also select specific protocols (DoH, UDP, or TCP) that are supported by the external DNS service and configure policies to ensure that your organization's DNS traffic is sent to the external DNS service from the Zscaler service only using those protocols. If the incoming DNS request uses a protocol that is different from the configured server-side protocol, the Zscaler service performs the necessary protocol translation and sends the DNS request to the external DNS service. Then the Zscaler service extracts the response from the DNS server, applies any configured policies, and forwards the response to the client using the inbound query protocol.
DNS Gateway provides the following benefits and enables you to:
- Ensure the high availability of the DNS service used by your organization by configuring primary and secondary DNS services.
- Perform DNS protocol translation to forward DNS queries to the external DNS service over DoH, UDP, or TCP, depending on requirements. With this protocol translation, the Zscaler service can encrypt users’ unencrypted DNS queries and send them to the external DNS service using DoH. In addition, protocol translation allows you to meet DNS compatibility requirements with the external DNS service.
- Define DNS filtering and NAT control policies to leverage and extend existing functionalities into comprehensive DNS Control.
- Ensure compliance with regulatory and contractual requirements like employing Protective DNS service.
DNS High Availability
When both primary and secondary DNS resolvers are configured, the Zscaler service can maintain DNS high availability by continuously monitoring the health and availability of the primary server and allowing failover to the secondary server if the primary server is unavailable.
When both primary and secondary DNS resolvers are configured, the Zscaler service can maintain DNS high availability by actively checking responses from the DNS server to determine the health and availability status of the server and by allowing failover to the secondary server if the primary server is unavailable. The service determines the server's health status using various parameters including:
- The server is not reachable and the connection to the server times out or fails
- The FQDN configured for the server is unresolvable
- The DoH server does not provide a DNS response (e.g., a web server that does not provide DoH service)
- The DNS server sends SERVFAIL or other response codes
- Response timeout occurs
When both primary and secondary DNS resolvers are configured in the DNS Gateway, the DNS requests are forwarded to the primary resolver. If the primary resolver does not return a response to a DNS query, then the primary resolver is considered unavailable, and the request is forwarded to the secondary resolver. If a response is received from the secondary resolver, all subsequent requests are forwarded to the secondary resolver.
If the secondary resolver also becomes unavailable, then the requests are forwarded to the primary resolver. This process of switching between primary and secondary resolvers comes to a halt when both resolvers fail to respond to a DNS query. Consequently, the DNS Gateway is marked as down, and the failover behavior configured in the gateway is triggered. The Zscaler service continues to probe the health of the DNS servers by sending inbound DNS queries periodically and resumes forwarding DNS queries to the server if one of the servers becomes available again.
DNS Protocol Translation
Translation to DoH allows you to encrypt your users' unencrypted DNS queries and send them to an external DNS service. The protocol translation functionality of the DNS Gateway extends beyond DNS encryption (using DoH) and enables organizations to be compliant with regulatory requirements, like safeguarding DNS with a Protective DNS service. Protective DNS is designed to shield organizations and users from DNS exploitation by preventing access to known malicious or suspicious sites using threat intelligence gathered from commercial providers, open sources, and governmental sources. By using the DNS Gateway, you can encrypt your users' unencrypted DNS queries and route them to any third-party DNS service using DoH.
The following table provides information on the supported DNS protocol translations:
| Protocol Translation | UDP to Server | TCP to Server | DoH to Server |
|---|---|---|---|
| UDP from Client | Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| TCP from Client | Not Supported | Supported | Supported |
| DoH from Client | Supported | Supported | Supported |
DNS Gateway Configuration
In the Admin Portal, you can configure a list of DNS Gateways with primary and secondary DNS services offered by your third-party DNS providers. Within the DNS Gateway object, you can configure the protocols over which DNS traffic can reach the configured services. After configuring the DNS Gateway, you can create DNS filtering rules to redirect traffic to the external DNS services over the specified protocol.
DNS Insights Logs provide visibility into the logs recorded for DNS traffic that is redirected to external resolvers via DNS Gateways. You can also track this data using interactive charts in the DNS Overview Dashboard.
The DNS Gateway feature is available with the Advanced Firewall subscription.
About the DNS Gateways Page
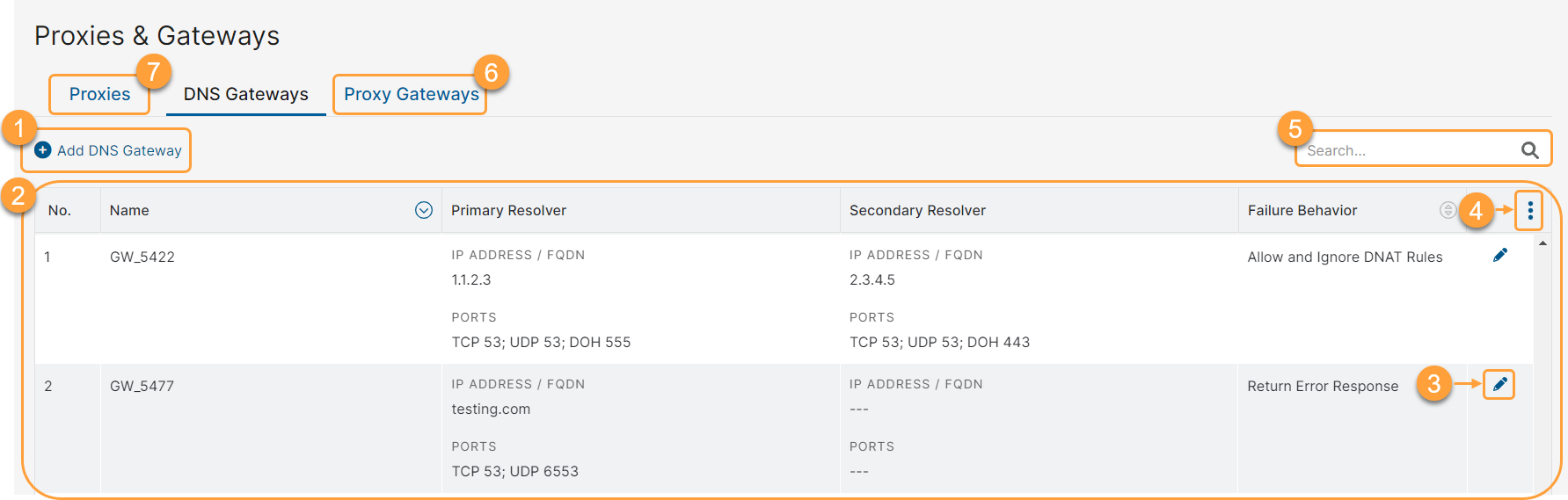
On the DNS Gateways page (Infrastructure > Internet & SaaS > Network Policies > Proxes and Gateways > DNS Gateways), you can do the following:
- Add a DNS Gateway.
View the list of configured DNS Gateways. By default, the table displays the following information:
- Name: The name of the DNS Gateway.
- Primary Resolver: Details of the primary DNS service, including the IP address or FQDN and the ports.
- Secondary Resolver: Details of the secondary DNS service, including the IP address or FQDN and the ports.
- Failure Behavior: The action configured to be performed when both primary and secondary resolvers are unavailable to serve the requests.
You can sort the table using the Gateway Name and Failure Behavior columns.
- Edit an existing DNS Gateway. You can also delete the DNS Gateway from the Edit DNS Gateway window.
- Modify the table and its columns.
- Search for a specific DNS Gateway using keywords.
- Go to the Proxy Gateways page.
- Go to the Proxies page.